What is forex leverage?
I know, forex leverage can be confusing and the fact that you are reading this right now means that you are a beginner trader just starting to learn about forex trading and the currency market.
As a matter of fact, it took me a while to understand the whole concept of leverage in forex.
In this post, you will learn about:
- What is forex leverage
- How leverage works in the forex exchange market
- The purpose for forex leverage
- How to calculate leverage
- What is the best leverage to select for your trading account size
Definition Of Leverage In Forex Market
The definition of leverage in forex is the ability to control a large amount of borrowed money while using a very little of you own money and expressed as a ratio of the amount of money borrowed to that of what you actually have.
A case of leverage applied in real life. Let me give an example…
Mary wants to buy a $300,000 house but she does not have the full amount to pay it so she puts down a 20% down payment of $60,000 on the house and she borrows from the bank the balance of $240,000.
Mary now controls a $300,000 house just by putting down $20,000.
Express as a ratio, Mary’s leverage will be $300,000:$60,000 = 5:1
A similar kind of situation happens in the forex market. A forex trader can deposit $1000 and he will be loaned $100,000. In this case, the leverage, again expressed as a ratio will be 100:1
Leverage Amounts
Forex brokers offer fixed leverage amounts but they can vary between brokers but these are usually the amounts: 30:1, 50:1, 100:1, 200:1 and 400:1.
European law regulated the maximum leverage at regulated brokers to 30:1.
What does each of these leveraged amounts mean?
50:1 Leverage
Fifty to one leverage means that for every $1 you have in your Forex trading account, you can place a trade worth $50.
As an example, if you deposited $500 into your trading account, you would be able to trade amounts up to $25,000 on the forex market using 50:1 leverage.
It’s not that you should be trading the full $25,000, but you would have the ability to trade up to that amount.
100:1 Leverage
One hundred to one leverage means that for every $1 you have in your Forex trading account, you can place a trade worth $100. The typical $2000 minimum deposit for a standard account would give you the ability to control $200,000.
200:1 Leverage
Two hundred to one leverage means that for every $1 you have in your forex trading account, you can place a trade worth $200. The typical minimum deposit on such an account is around $300. With $300 you would be able to open up trades up to the amount of $60,000.
400:1 Leverage
Four hundred to one leverage means that for every $1 you have in your forex trading account, you can place a trade worth $400.
What Is The Best Leverage To Select Based On Your Trading Account Size?
You’ve got to be careful about which size of leverage you choose for your trading account.
The big problem with forex leverage is the fact that the greater the amount of leverage on your trading capital, the higher the risk you will have. The opposite is also true, you can increase your trading account very quickly if you win in your trades.
That’s why they say forex leverage is a double-edged sword.
Now, you are not going to understand this but I’ve given an example below of how two traders using the same trading account size, using different size leverages have totally different outcomes.
At the end of the day, you have to make your own choice as to what leverage size is right for you.
The Purpose of Leverage In Forex Trading
So why would the forex broker give you control of $100,000 when you only put in $1,000? (100:1 leverage)
The reason why traders use leverage or rather, the forex brokers offer leverage is for you to make more money with a little of your own money.
So why are the forex brokers so kind in offering you large amounts of money to trade?
Aren’t they not risking their money?
The fact is, forex brokers don’t really have a lot of risk in offering you leveraged trading. They have strict risk management systems in place that take care of this automatically unless something unexpected like the CHF turmoil following the Swiss National Bank’s decision to end its capping of the Swiss Franc against the EURO which resulted in Alpari UK shutting down.
This is what Alpari UK Said:
“Where a client cannot cover this loss, it is passed on to us,”.
The real risk here is the money a trader puts into a trading account to trade. That money is to cover your trading losses and hardly the brokers’ money is touched.
How To Calculate Forex Leverage
Calculating leverage is really simple as I’ve shown above.

Forex brokers require what is called a margin to be deposited in your trading account before you can buy or sell currencies. If 1% is required of the total value of the trade, then if you want to trade one standard lot of USDCHF, which is equivalent to US $100,000, then your margin will be 1% of US $100,000 = $1,000.
Only when $1,000 margin is sitting in your forex trading account then you can open a 1 standard lot contract trade on USDCHF.
So in this example here, the leverage expressed as a ratio would be 100:1
How Leverage Works In The Forex Market
I know you will not understand this at first so let me give you a simple example of how forex leverage works in real trading situations.
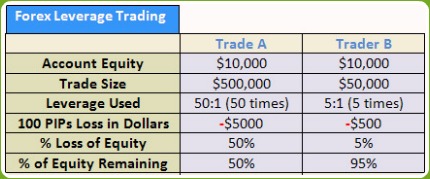
The table below gives a comparison of two traders, A & B but before that let’s say that:
- Each has the same trading account size of $10,000
- Trader A uses a leverage of 50:1 and decides to open a $500,00 trade size (equates to a 5 standard lot trade…you divide $500,000 trade size by $100,000 per standard lot trade size gives you the answer 5 standard lots).
- Trader B, being more careful uses a leverage of 5:1 and opens a trade size of $50,000 (equates to 0.5 lot trader…or half a standard lot trade).
- Both traders open sell trades of USDCHF at the price of 1.1000
- 1 pip of USDCHF for one standard lot = $10.
- Each place has a 100 pips stop loss.
- After they place their sell trade, instead of the price moving down so they can profit in their trades, the price of USDCHF moves up 100 pips to USDCHF=1.1100
What is the total loss of Trader A?
5 standard contracts x 100 pips stop loss x $10 per pip = $5,000 LOSS
What is the total loss of Trade B?
0.5 lots x 100 pips stop loss x $10 per pip= $500 LOSS
From the table above, you can see that Trader A lost 50% of his trading account whilst Trade B only lost 5%.
Now, imagine if the price of USDCHF moved up 100 pips instead of down and hit a profit target of 100 pips. What would have happened?
Trade A would make a whooping $5000 profit which would be a 50% trading account increase whilst trade B would only make a $500 profit on his trade which would only be a 5% trading account increase.
This example shows that forex leverage can be a very good friend if you learn to manage it properly, but can be your worst enemy if you do not know how to play with it.
Are you looking for a broker that offers high leverage? Check out the Best Brokers List.